Hybrid Solar System: A Smarter Approach to Sustainable Energy
The off-grid system gives you uninterrupted electricity during blackouts, while the cost-effective on-grid system enables you to sell the excess electricity unit. The drawbacks of both systems pushed the creators to create a system with dual functionality. The result was a system that could be both an off-grid and on grid system, possessing all the salient features of either. These days, hybrid solar system comes in various shapes and sizes and integrate solar and battery storage into one unit. now in pakistan solar panels prices decrease to 29 rupees per watt it is fortune to install solar system for agri and home.
Because battery storage is becoming more affordable, systems already connected to the electrical grid can also start to profit from it. To do this, you must be able to store solar energy generated during the day and use it at night. Customers can benefit from the best of both worlds because the grid is available as a backup when the stored energy is used up. Hybrid solar system can also use inexpensive off-peak electricity (often available from midnight to six in the morning) to charge the batteries.
Workings of a hybrid solar system
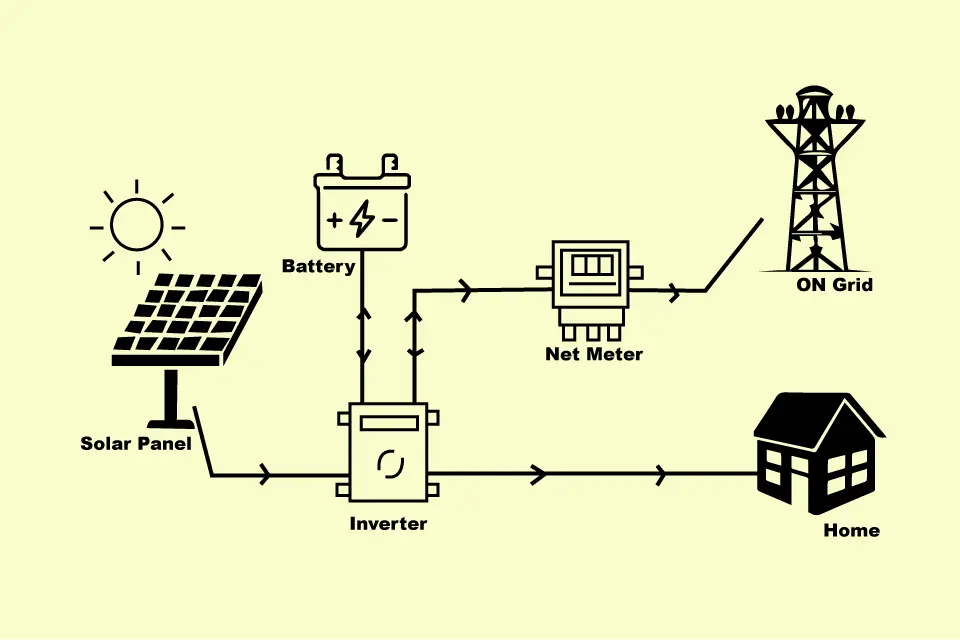
Hybrid system design can also take many forms, but we’ll keep things basic for this discussion. See our comprehensive guide to residential solar battery systems for additional information on the various hybrid and off-grid power options. In a hybrid solar system, any extra solar energy that is not needed for your property’s appliances is sent to the battery bank.
After that, you can drain the battery’s energy and utilize it to power your house—usually in the evening peak when electricity prices are at their greatest. The grid of electricity and the meter. You can use your meter to export solar electricity not used by your application, depending on how your hybrid solar system is configured and whether your utility permits it.
How Does a Hybrid Solar System Work?
While hybrid solar system store energy for later use with special hybrid inverters and batteries, they nonetheless produce power like a conventional grid-tied solar system. Like a traditional grid-tied solar system, hybrid solar systems produce electricity and employ specialized hybrid inverters and batteries to store energy for later use.
Like a UPS system, most hybrid solar systems can also be a backup power supply during a blackout due to their energy storage capacity.The term “hybrid” in the solar business describes a system that can interface with the electrical grid and includes solar and batteries.
Combines solar and batteries and can communicate with the electrical grid. When your batteries are fully charged, historically, you may turn them on to the grid. Your appliances will start pulling power from the grid when they are not using your solar system or when the usable power in your batteries runs out. Hybrid describes power sources that use two sources, like solar and wind.
Featured in Hybrid Solar System
Electricity Production
When daylight energizes the electrons in the PV cells, they produce power, much like the other two solar panel systems. It causes them to produce current, which is subsequently transferred to the inverter by a connecting network.
Transition
The hybrid solar inverter converts the electrical power produced as direct current to alternating current. The home is then connected to this 240-volt alternating current.
keeping of electricity
Until the batteries are fully charged to their maximum capacity, all the abundant power is stored in them.
Using Net Metering
The extra power is sent to the utility grid system via Net Metering when the batteries run low. It enables users to receive credits for the energy they supplied and apply the credit amount to their account.
System Ready for Batteries
In contrast to a traditional string solar inverter, a hybrid inverter is utilized in “battery-ready” systems. The battery charger and connector are already included in most contemporary hybrid inverters, simplifying future battery additions. It is important to note that hybrid inverters are more costly and that while technology is developing quickly, locating appropriate batteries within a few years may become challenging if you don’t include them during the first installation. When storing solar energy.
Why use batteries?
Many countries and network providers have reduced solar energy’s feed-in tariff (FiT).
Typical grid-feed solar systems are less appealing as most people are away during the day to use the generated solar energy. The energy is thus supplied into the system for comparatively little return.
. Besides storing extra solar energy, a solar hybrid system may supply backup power during a blackout.
It is ideal for homeowners, but a typical grid-feed solar system is still the most cost-effective option for most businesses open during the day.
With hybrid solar systems, you can store solar energy for usage in the evening, when electricity prices are usually at their highest.
Self-use or self-consumption is the capacity to store and utilize your solar energy as needed. It functions similarly to an off-grid power system.
Still, it requires a much less battery capacity—typically only enough to meet peak usage for eight hours or fewer, as opposed to 3-5 days for an off-grid system.
Does adding batteries require a hybrid inverter?
The short response is no. With what is referred to as an AC battery system, a battery can be added at any moment to any existing grid-tied solar system. Access to a wider range of options is growing, and AC batteries such as the Tesla Powerwall 2 are gaining popularity. Given the quick advancements in inverter and battery technology, spending extra money on a “battery-ready system” may not be worth spending extra money unless you intend to install a battery within the next two years.
Benefits of Battery Storage:
- It lets you store extra solar energy or is inexpensive. Permits the use of solar energy stored during evening peak hours.
- The majority of hybrids can provide backup power.
- Low the bill of electricity drawn from the grid.
- Allows for sophisticated energy management, such as peak shaving.
- Because these systems can draw additional electricity from the grid and continue to provide electricity in the event of load shedding, they are the most dependable when handling power outages.
- These systems also come with the Net Metering option.
The drawbacks of Battery Storage Systems
- It has higher prices, mostly due to batteries’ high price.
- Extended payback period – Increased return on investment
- More space and a higher installation cost are needed for more sophisticated installations.
- 7 to 15 years of battery life.
- Depending on the type and capacity of the hybrid inverter, the amount of appliances you can run simultaneously while using backup power may be limited.